Effects of Misinformation on Online Discussions
CSH Friday talk
Jula Luehring
14 June 2024
Misinformation and emotions


Do (arousing) emotions make people believe in misinformation?
Emotional state ![]()
Replication study
False/accurate COVID-19 news headlines
Austria 2021
N = 422

\(\rightarrow\) No effects of emotional state on misinformation acceptance
Emotional response
\(\rightarrow\) More anger and less joy in response to false news
🗯 “Bullshit”, “Fake”
\(\rightarrow\) Function of emotion depends on existing beliefs

Problem #1
Different effects of emotions are overlooked by
mixing up different timings of emotions,
ignoring the function of emotions,
measuring positive and negative sentiment only.
Misinformation on social media
Collective dynamics online
Moralizing and arousing content gets high engagement
Misinformation: conflict and negative
- But: only 0.3-6% in 5 studies from 2016-2021
- Elite and ordinary partisan superspreaders
\(\rightarrow\) Misinformation is embedded in partisan intergroup dynamics
\(\rightarrow\) Secondary effects?

What are the effects of misinformation on discussions?
But: how to identify misinformation?

\(\rightarrow\) How do these choices influence downstream research results?
Luehring, Lasser et al., (in prep.)
Problem #2
Misinformation is measured as clearly true or false instances,
neglecting less extreme types,
making it hard to isolate effects of misinformation.
Our objectives
- Collecting a systematic, large-scale and long-term data set for the German-speaking context
Continuous trustworthiness ratings by NewsGuard (#1)
- Approximating causal inference to test the effects of misinformation on emotions
Nonparametric matching strategy (#2)
Data collection
Posts from Twitter/X mentioning any of 347 German news domains
N = 9.3M discussions (20.6M tweets total)
93.8% trustworthy (>60)
Machine learning classification
pol_emo_mDeBERTa (Widmann & Wich, 2022; Macro F1=0.7)
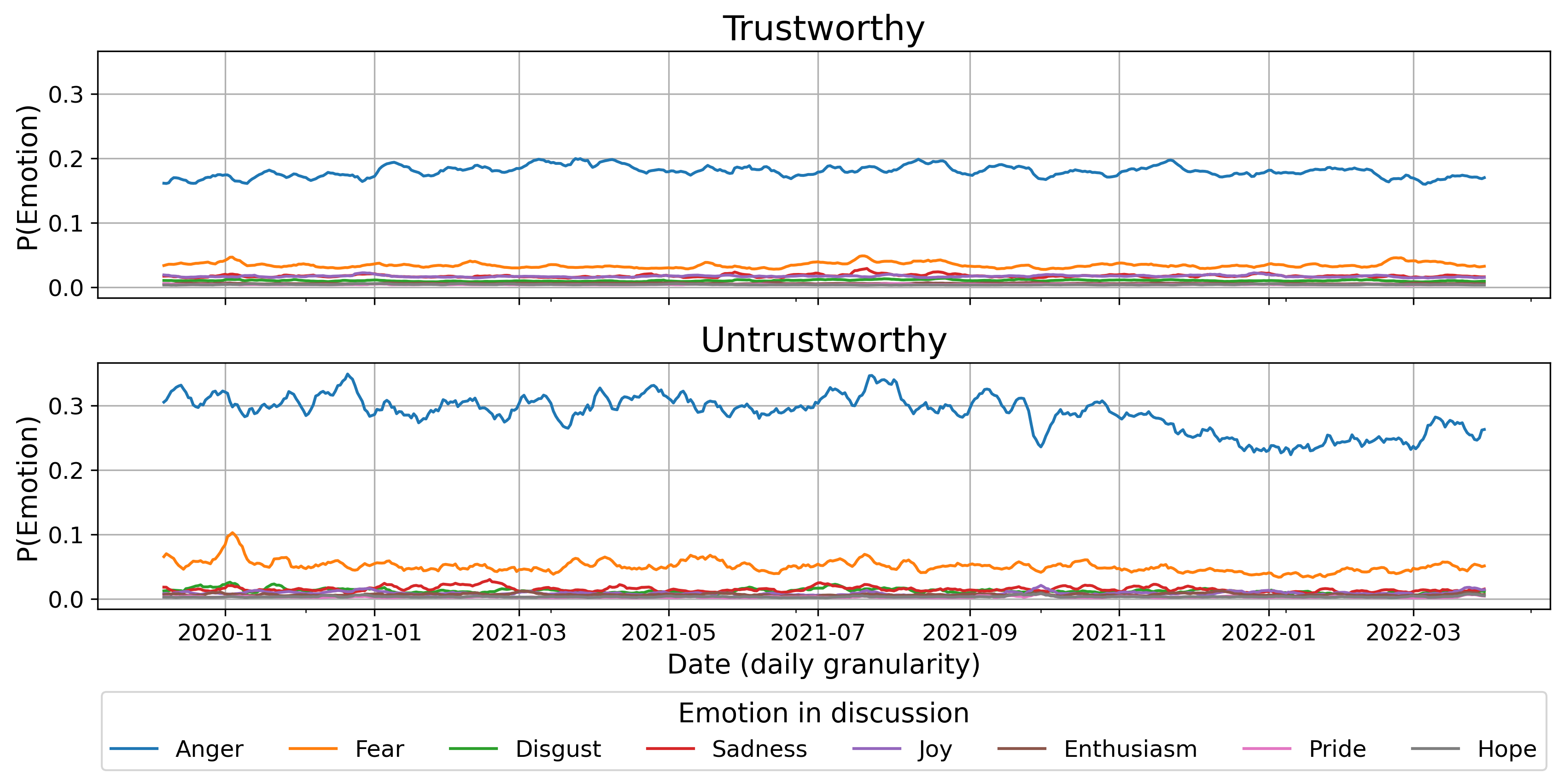
Part I: Emotion in the post
Is trustworthiness associated with anger?
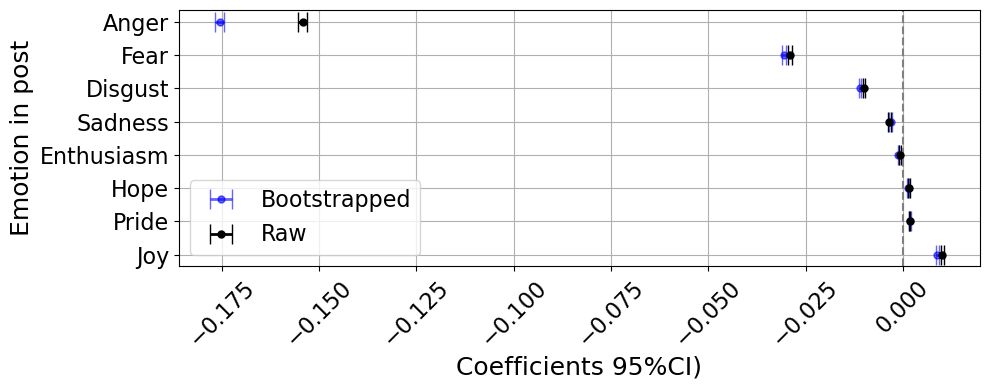
\(\rightarrow\) Trustworthiness predicts a 15% decrease in anger

But gray-area content matters, too!
Part II: Engagement
Is lower trustworthiness associated with higher engagement?
Models: Zero-inflated Negative Binomial (log-link)
Controls: PO, word count, following, initial emotions


\(\rightarrow\) 58% decrease in retweets and 43% decrease in quotes
Zeileis et al., 2008
Part III: Emotional responses
A) Correlations
Emotional response reflects emotion in post
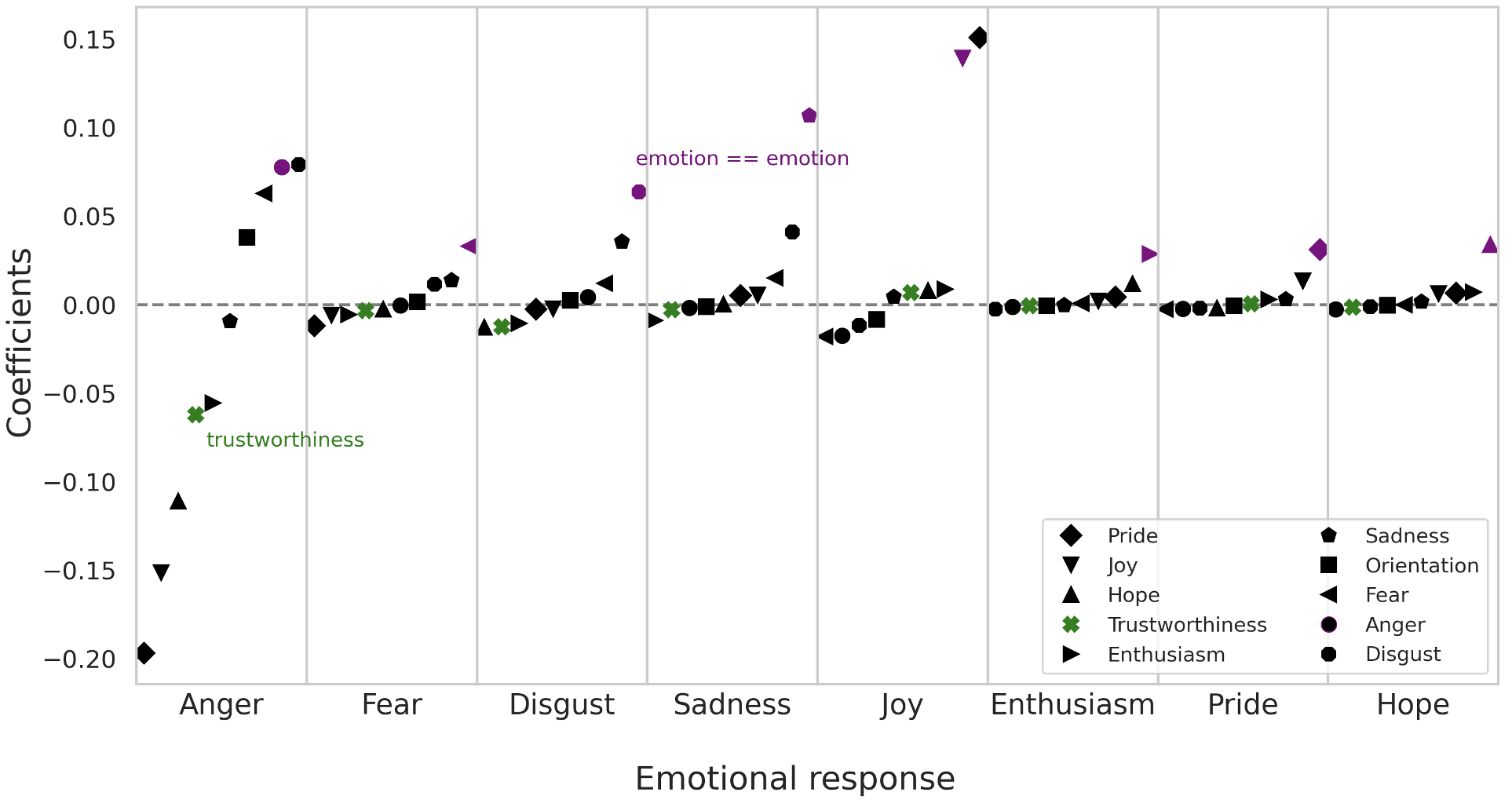
\(\rightarrow\) Does trustworthiness actually affect emotional reactions?
B) Causal inference

Nonparametric matching

Nearest Neighbor and Mahalanobis distance
\(\rightarrow\) N = 87,132
Ho et al., 2007
Does trustworthiness affect emotional responses?
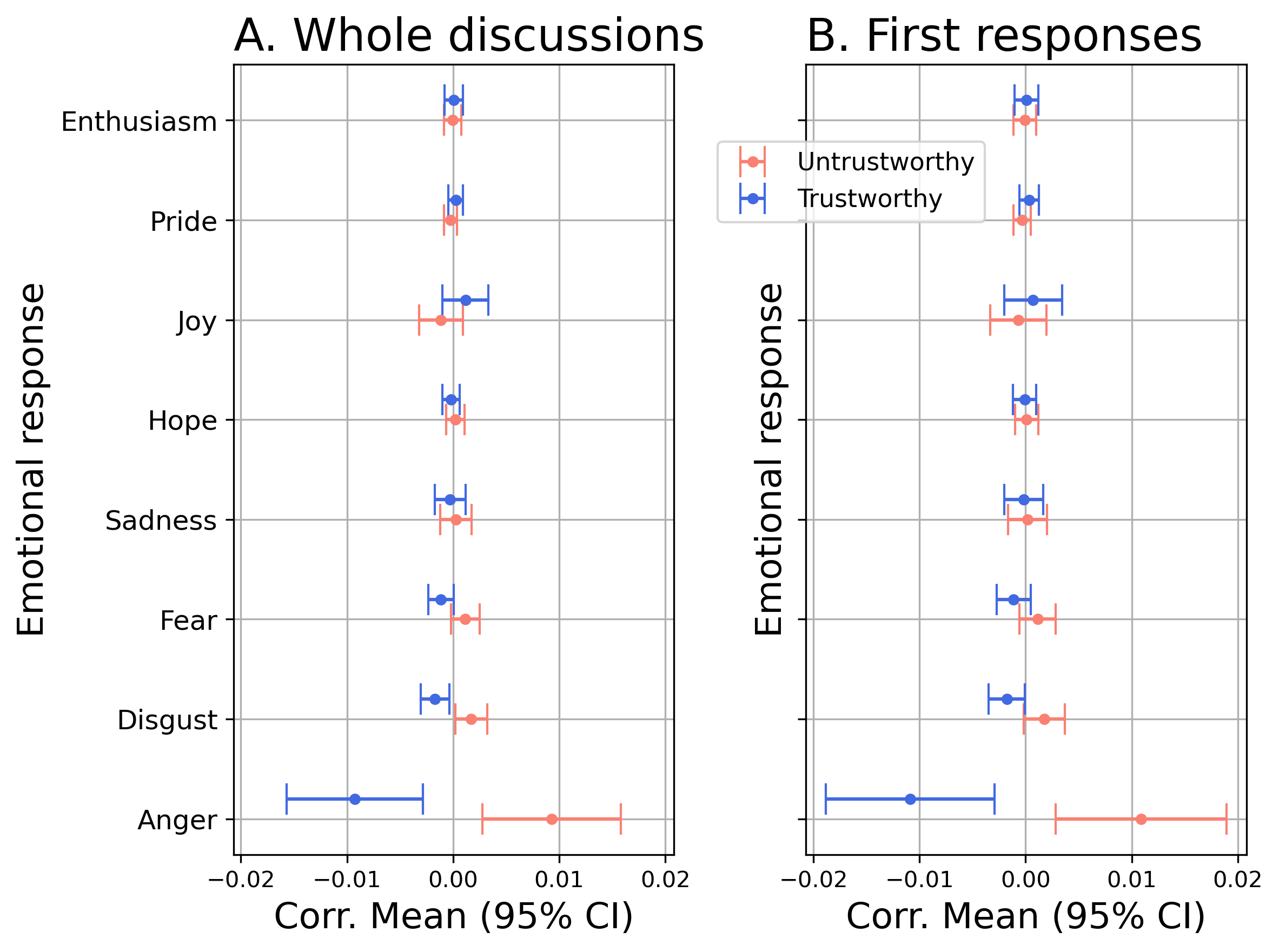
\(\rightarrow\) Less joy
\(\rightarrow\) 2% more anger
TBD: responses within-users (responding to trustworthy and untrustworthy posts), see Carrella et al., 2023
C) Direction of anger (TBD)
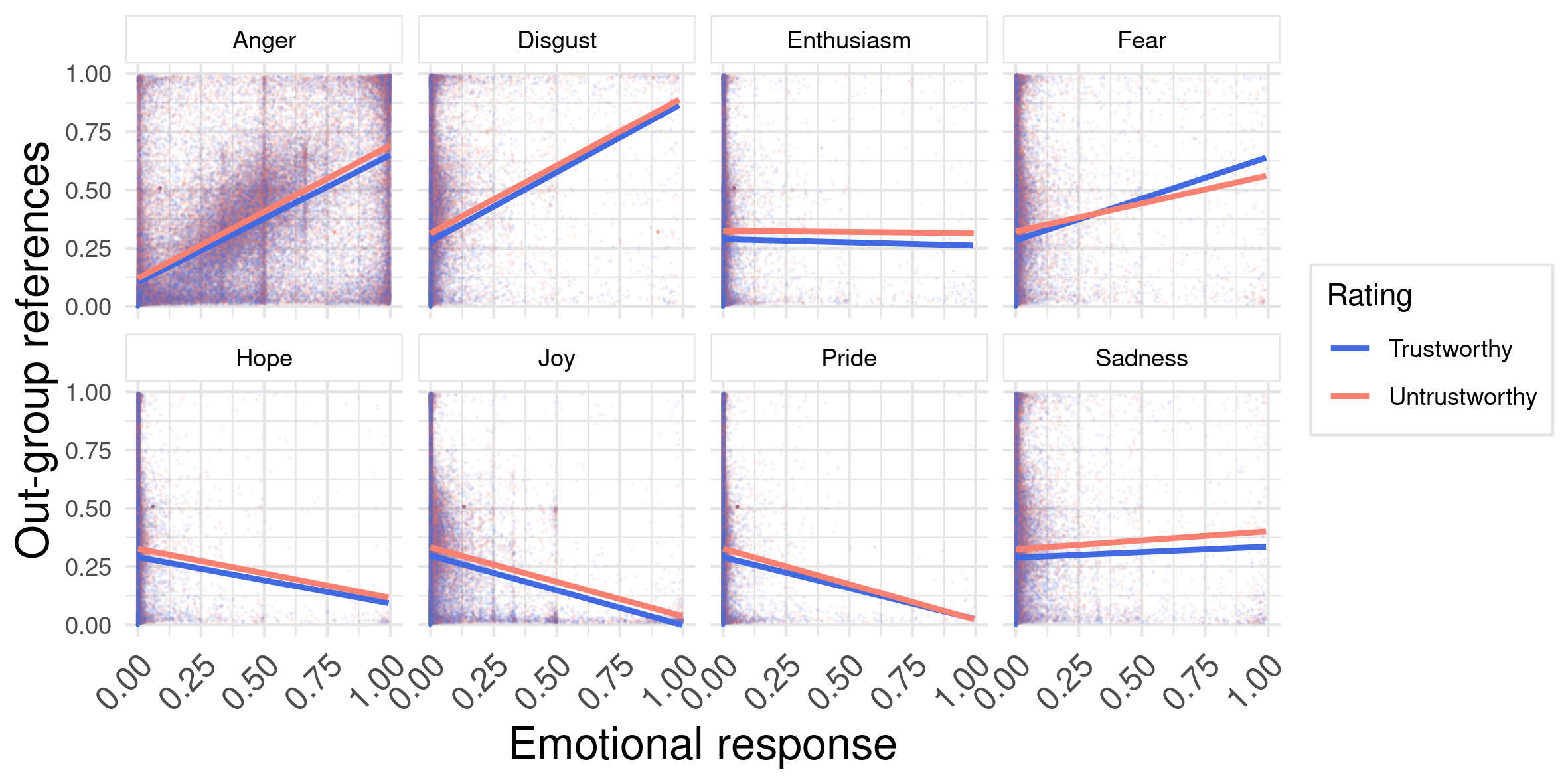 Out-group classification (Lasser at al., 2023; F1=0.8)
Out-group classification (Lasser at al., 2023; F1=0.8)
C) Origin of anger (TBD)
- How do people talk in most angry discussions? Do they counterargue?
What are the topics in the first post?
Do the discussion networks differ (see Gonzalez-Bailon et al., 2010)?
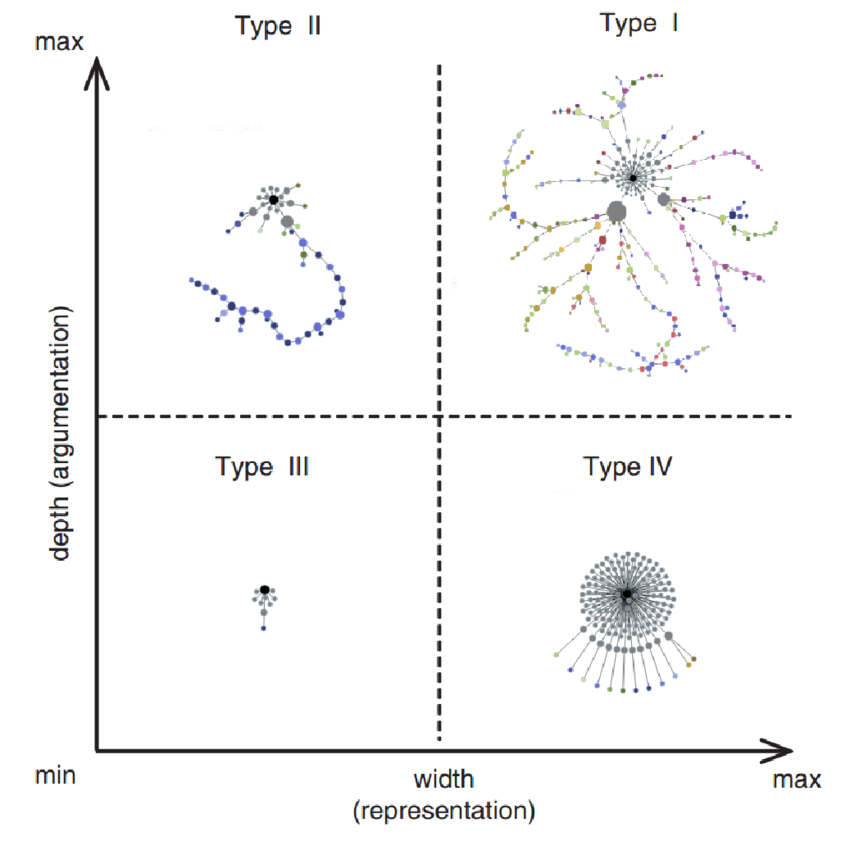
Conclusion (tentative)
Emotions \(\rightarrow\) emotions \(\rightarrow\) engagement?
- Sources with low trustworthiness predict anger
- Emotions in discussions largely reflect emotions in initial post
- Is engagement with low trustworthiness due to other factors?
\(\rightarrow\) Not the factfulness is harmful, but the content
\(\rightarrow\) Misinformation is a perfect tool to spread hateful content
Thank you!

Is lower trustworthiness associated with higher engagement?
Models: Zero-inflated Negative Binomial (log-link)
Controls: PO, word count, following, initial emotions


Zeileis et al., 2008


